
Are you preparing for a C interview? Feeling excited but quite nervous at the same time? fear not. This comprehensive guide is here to guide you to demonstrate a solid grasp of C concepts, help you to grow your problem-solving skills, and also make you feel confident to ace your interview.
Keep in mind for a good communicative interview Sometimes be in the interviewer's shoes too, Don't just answer, ask! Show your genuine interest by crafting insightful questions about the company, role, and team.
Explore the depth of C programming with our comprehensive guide to 50 C Interview Questions and Answers. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, this resource provides valuable insights, helping you master essential concepts and excel in C-related interviews.
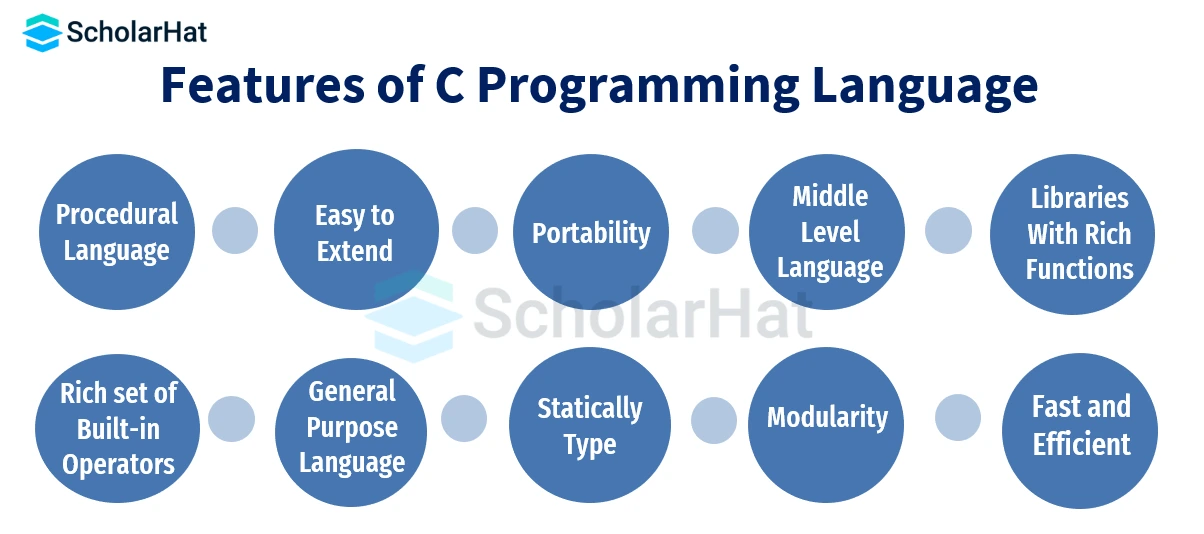
C possesses features of both lower-level and higher-level, or assembly-level, languages. C is hence frequently referred to be a middle-level language. One may write both a menu-driven consumer billing system and an operating system in C.

Printf()- To print the output to the screen, use print().
Scanf()- To read formatted data from the keyboard, use scanf().
The answer is "f". In C-style languages, the expression 5["zyzuv"] is equivalent to "zyzuv"[5], which accesses the 6th character of the string "zyzuv". Therefore, the value of the expression is "v".
The built-in C functions scanf(), printf(), strcpy, strlwr, strcmp, strlen, strcat, and many more are used often.
The term "built-function" refers to library functions that the system provides to developers to help them with specific frequently performed predefined tasks, hence simplifying their lives. For instance, printf() in C is used when you need to print your program's output to the terminal.
A software application known as a preprocessor is used to handle source files before submitting them to be built. The preprocessor allows for the inclusion of header files, macro expansions, conditional compilation, and line control.
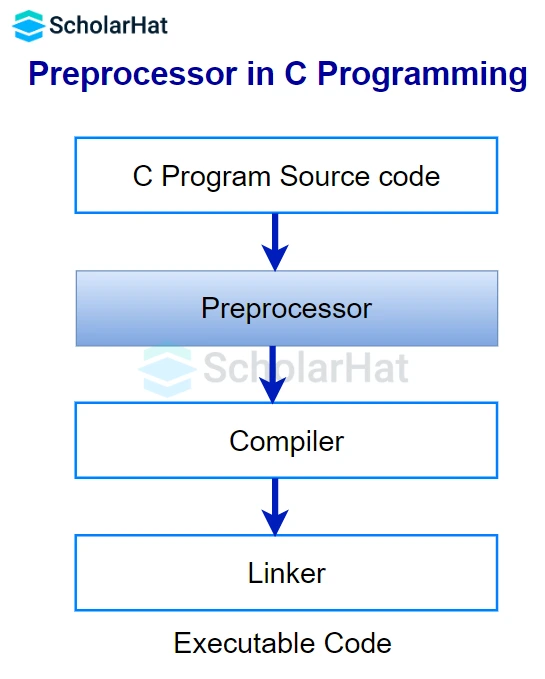
Preprocessor directives in C are built-in predefined functions or macros that are performed before program execution and serve as instructions to the compiler. The process of creating and running a C program involves several phases. Macros, File Inclusion, Conditional Compilation, and Other directives like #undef, #pragma, etc. are the main categories of Preprocessor Directives.
In the C programming language, data values are preserved across function calls even after they have exited their scope thanks to the usage of static variables. Static variables don't require initialization each time they are used in a program; their values are preserved inside their scope. Without initialization, the initial value of a static variable is set to 0.
< , var); , x);
The library methods malloc() and calloc() are used to allocate dynamic memory. The memory that is allocated from the heap section while the program is running is known as dynamic memory. The header file "stdlib.h" is what makes dynamic memory allocation in the C programming language possible.
Recursion in C is a programming technique where a function calls itself directly or indirectly to solve a problem. In recursive functions, the function breaks down the problem into smaller subproblems and calls itself with modified arguments until a base case is reached, stopping the recursive calls.
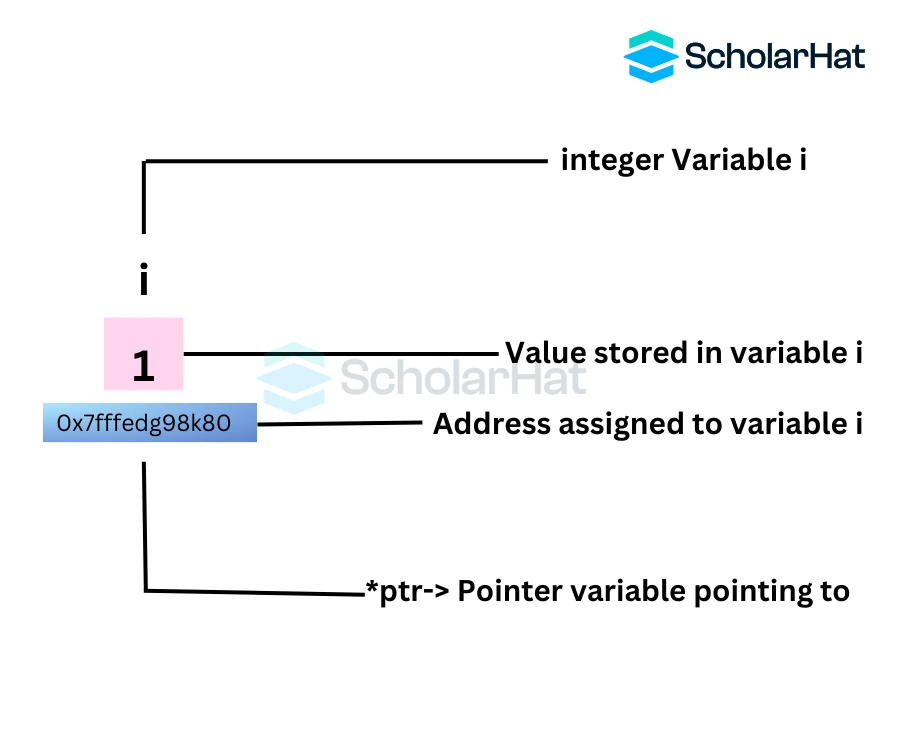
A pointer in C is a variable that holds the memory address of another variable. It allows direct manipulation of memory locations, enabling dynamic memory allocation, efficient array handling, and indirect access to data. Pointers are a fundamental feature used for tasks like data structures and dynamic memory management.
Loops in C are programming constructs that repeatedly execute a block of code as long as a specified condition is true. They enable efficient iteration through data, simplifying tasks like array manipulation or repetitive operations, ensuring code efficiency and maintainability. Common loop types in C include for, while, and do-while.
Let's see how we create infinite loop in C
In C, a pointer to a pointer, also known as a double pointer, is a variable that holds the address of another pointer variable. It allows indirect access to a memory location, providing a way to modify pointers and dynamically allocate multi-dimensional arrays, enhancing flexibility in memory management and data structures.
Typecasting in C is the process of converting one data type into another. It allows a variable to be treated as a different type temporarily. For example, converting an integer to a float or a pointer from one data type to another is done using typecasting operators like (float) or (int*).
(data_type)expression;The given C code in theC Online Compiler initializes an integer variable x with the value 97 and then uses a for loop to print the characters corresponding to ASCII values from 97 to 122. In the ASCII table, these values represent lowercase English letters from 'a' to 'z'.
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzIn C programming, header files are files containing function declarations and macro definitions. They allow code reuse by providing function prototypes to other source files. Commonly used header files include for input/output functions and for memory allocation functions.
Header files in C serve several purposes:
A pre-processor command that designates a group of C statements is called a macro. The pre-processor directive defines a macro. Since macros are preprocessed, our program would not have been compiled until after all of the macros had been preprocessed. Functions are compiled rather than preprocessed, though.
There are two primary techniques in C for converting strings to numbers: string streams and the stoi() and atoi() library functions.
Instead of using normal input, it reads data from a string.
This method returns an integer value when it receives a character array or a string literal as input.
In a program, each keyword is designed to carry out a certain function. They cannot be used for reasons other than those for which they were designed since their meaning has already been established. The programming language C has 32 keywords supported. Reserved keywords include things like auto, else, if, long, int, switch, typedef, and so on.
In C, a structure is a user-defined data type that allows you to group variables of different data types under a single name. It is used to represent a record containing different fields, enabling you to store and manipulate related data more efficiently. Example
student < ; student obj; ); , obj.name); , obj.roll_no); , obj.address); , obj.branch);
The given C program in C Editor defines a structure student with member name, roll_no, address, and branch. It then creates an object of this structure, initializes its members, and prints the values of these members
Name: Urmi_Bose Roll_No: In C, a union is a user-defined data type that allows different data types to be stored in the same memory location. Unlike structures, unions use the same memory space for all members, allowing only one member to hold a value at any given time. Unions are often used to save memory when different data types need to share the same memory location.
name_of_union < data_type name; data_type name; >;
When an object has an address or a unique position in memory, it is referred to as an "l-value." Either the left or right side of the assignment operator(=) will display a "l-value." A data value kept in memory at a specific location is called a "r-value." An object without a known location in memory is referred to as an "r-value" (i.e. without an address). An expression that cannot have a value assigned to it is known as a "r-value," and it can only appear on the right side of an assignment operator (=).
val is the ‘l-value’, In C, call by value is a method of passing arguments to functions. When a function is called with parameters, the values of the parameters are copied into the function's parameters. Any modifications made to the parameters inside the function do not affect the original values outside the function.
Call by reference in C involves passing the memory address of a variable to a function, allowing the function to modify the actual value at that address. Changes made to the parameter inside the function are reflected outside the function, as the function operates on the original data in memory.
Certainly, here are the differences between call by value and call by reference in C:
In C, enumerations (enums) are user-defined data types that consist of a set of named integer constants. Enums provide a way to create symbolic names (enumerators) for integral values, making code more readable and understandable. Enums are often used to define sets of related integer values with meaningful names.
enumeration_name;include Days < SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY >; < Days today; today = WEDNESDAY; ); ); Run Code >>
In this code in the C Online Editor, an enumeration Days is defined with the days of the week. The program sets the today variable to WEDNESDAY and prints the corresponding day using a switch statement.
Today is: Wednesday < , third); > ); ); , ); , , third); first = second; second = third; >
Please Enter number of Elements:
; Run Code >>
Static memory allocation- Static memory allocation is the type of memory allocation that occurs during compilation. Allocating static memory reduces operating time. Because memory is allocated from the stack, it is quicker than dynamic memory allocation. Compared to dynamic memory allocation, this form of memory allocation is less effective. Within the array, it is mostly favored.
Dynamic memory allocation- Dynamic memory allocation is the process of allocating memory during runtime or execution. Because dynamic memory allocation uses the heap for memory allocation, it is slower than static memory allocation. When compared to static memory allocation, this form of memory allocation is more efficient. Most people in the linked list favor it.
Depending on the size of the data type, assigning a variable requires space in either our heap or RAM. Nevertheless, if a programmer uses heap memory and forgets to delta it, eventually all of the RAM's memory will be used up and there won't be any more memory, which could result in a memory leak.
Run Code >>
You can track every memory allocation you make, plan to the point where you wish to destroy (in a good sense) that memory, and then remove it there to prevent memory leaks. Using the C++ smart pointer in C to connect it to GNU compilers is an additional method.
typedef in C is used to create custom data type aliases. It allows programmers to define names for existing data types, making the code more readable and adaptable. Custom types created with typedef can simplify complex declarations and enhance code clarity.
An alias name for the current complex type definition is provided by typedef. You may easily make an alias for any type with typedef. Typedef will let you write shorter code, whether you're declaring a sophisticated function pointer, structure, or simple integer.
); > , num); > , num); >
This C program checks whether a given number is prime or not. It takes an input number, iterates from 2 to the square root of the input, and checks for divisibility. If the number is divisible by any value in this range, it's not prime. If it's less than or equal to 1, it's not prime either. The result is displayed accordingly.
A function that uses pass-by-reference can change a variable without copying it. Since the provided parameter and variable share the same memory address, any modifications made to the argument will also affect the variables.
< *num = , num); , num);
In this code, the change function takes a pointer to an integer as a parameter and modifies the value stored at that memory location. The address of the num variable is passed to the change function using the & operator. As a result, the value of num inside the main function is changed to 34.
Value of num before passing is: Value of num after changing with the help of function is:
In the C programming language, each local variable in a function is referred to as an automatic variable. For every variable declared inside a function or block, the default storage class is Auto. Access to auto variables is restricted to the block or function in which they have been defined. With the aid of pointers, we may use them outside of their intended usage. Auto keywords by default have a garbage value.
This code uses the printf function inside the if statement condition. The printf function returns the number of characters printed. Since the string "Hello - World" has a non-zero length, the condition evaluates to true and the empty block < >under if is executed, leading to the printing of "Hello - World".
Hello - WorldThis C program calculates the factorial of a given number using recursion. The factorial function recursively calculates the factorial: n! = n * (n-1)!. In the main function, the program calculates the factorial of 5. The program computes 5! Which is equal to 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1 = 120, and prints the result.
Factorial of ?
In C programming, both #include ". " and #include <. >are used to include header files, but they differ in their search paths and usage:
#include ". " (Double Quotes): The C preprocessor searches the predefined list of system directories for the filename before checking user-specified directories (directories can be added to the predefined list by using the -I option).
#include <. >(Angle Brackets): The preprocessor follows the search path given for the #include form after first searching in the same directory as the file containing the directive. Include programmer-defined header files using this way.
Using double quotes (". ") is generally preferred for including project-specific headers, while angle brackets (<. >) are used for standard library or system headers to distinguish between user-defined and system-provided header files.
); , var); > , var); >
This C program checks if a given number is an Armstrong number or not. It calculates the sum of cubes of its digits and compares it with the original number. If they are equal, it's an Armstrong number. 1^3 + 5^3 + 3^3 = 153, which matches the original number.
include Node < Node* next; >; Node* data < list2->data) < list1->next = next = next); > Node* Node* newNode = (data = data; newNode->next = < , node->data); node = node->next; > < Node* list1 = next = next->next = Node* list2 = next = next->next = ); ); Node* mergedList = ); Run Code >>
In this program, two sorted linked lists (list1 and list2) are merged into a new sorted linked list (mergedList). The merged list is then printed.
First sorted linked list: In the C language, the extern keyword is used to increase the visibility of C variables and functions. External can be shortened to extern. When a specific file wants to access a variable from any other file, it is used. Variables containing the extern keyword are simply declared, not defined, which increases duplication. There is no need to declare or create extern functions because they are visible by default throughout the program.
Note: getch() and getche() are not standard C functions and are not recommended for portable and modern C programming. Prefer using getc() or getchar() for standard and portable input operations.
Import is a keyword, but #include is a statement processed by pre-processor software. #include increases in the size of the code.
In conclusion, mastering these top 50 C language interview questions is pivotal for aspiring programmers. These insights into fundamental concepts, data structures, and algorithms equip candidates with the knowledge needed to succeed in technical interviews. Practice, understanding, and confidence in these areas will undoubtedly pave the way to a successful C programming career. You can also consider doing our C programming tutorial from ScholarHat to upskill your career.
C interview questions can range from basic syntax and data types to complex memory management and design patterns. They are typically categorized as:
To prepare for a C programming interview, it's essential to review core concepts such as data types, operators, arrays, pointers, and memory management. Additionally, practice solving coding problems and familiarize yourself with common algorithms and data structures implemented in C.
In a C interview, you can expect a mix of theoretical questions to assess your understanding of concepts and practical coding problems to evaluate your problem-solving skills. Questions may range from basic syntax and language features to more complex algorithms and data manipulation tasks.
Improving problem-solving skills for C interview questions involves regular practice and exposure to a variety of coding challenges. Utilize online platforms, coding competitions, and resources such as textbooks and tutorials to enhance your problem-solving abilities.